שאול קמחי ואח', 2023-2024. חוסן האוכלוסיה ומדדי התמודדות, מלחמת חרבות ברזל
מחקר זה מתמקד בשינויים במשתני המחקר: חוסן, מדדי התמודדות חיוביים ושליליים במדידות חוזרות שנערכו במהלך מלחמת "חרבות ברזל". להלן חמישה דו"חות ראשונים של המחקר:
קמחי, ש., מרציאנו, ה. אשל, י., קאים, א. ועדיני, ב. (ספטמבר 2024). חוסן ומדדי התמודדות לאורך המלחמה: מדידת אורך חמישית
קמחי, ש., מרציאנו, ה. אשל, י., קאים, א. ועדיני, ב. (אפריל 2024). חוסן ומדדי התמודדות - בעקבות התקיפה האיראנית: מדידת אורך רביעית
קמחי, ש., אשל, י., מרציאנו, ה. ועדיני, ב. (אוקטובר 2023). חוסן האוכלוסייה במדינת ישראל בשבוע הראשון של מלחמת "חרבות ברזל "
קמחי, ש., אשל, י., מרציאנו, ה. ועדיני, ב. (נובמבר 2023). חוסן האוכלוסייה ומדדי התמודדות - מדידת אורך שנייה, לאחר שבעה שבועות של המלחמה בעזה
קמחי, ש., אשל, י., מרציאנו, ה., קאים, א. ועדיני, ב. (ינואר 2024) חוסן האוכלוסייה ומדדי התמודדות לאורך שלוש מדידות חוזרות במהלך המלחמה הנוכחית
לפרסומים קודמים, ראו:
קמחי, ש. ושמאי, מ, (2006). חוסן קהילתי כבולם תגובות לחץ: תגובות תושבי הצפון ליציאת צה"ל מלבנון. סוגיות חברתיות בישראל (1) 152-170
דו"חות מחקר
קמחי, ש., מרציאנו, ה., אשל, י., (2018). מדד החוסן לישראל – יוני 2018
קמחי, ש., מרציאנו, ה., אשל, י.ת (2019). מחקר החוסן במועצה האזורית גליל עליון
קמחי, ש., עדיני, ב., מרציאנו, ה., אשל, י., (2019). מדד החוסן בעקבות סבב "חגורה שחורה"
קמחי, ש., מרציאנו, ה., אשל, י., עדיני, ב., (2020). חוסן בימי קורונה
קמחי, ש., מרציאנו, ה., אשל, י., עדיני, ב., (2020). חוסן ודחק בימי קורונה במועצה האזורית גליל עליון
קמחי, ש., מרציאנו, ה., אשל, י., עדיני, ב., (2020). חוסן ודחק בימי קורונה ביישוב ביהודה ושומרון
קמחי, ש., מרציאנו, ה., אשל, י., עדיני, ב., (2020). ישראל בעקבות ההתפרצות המחודשת של מגפת הקורונה: ירידה בחוסן
קמחי, ש., מרציאנו, ה., אשל, י., עדיני, ב., (2020). חוסן ודחק במגפת הקורונה: מדידת אורך שלישית
קמחי, ש., מרציאנו, ה., אשל, י., עדיני, ב., (2021). חוסן, מיטביות ודחק במגפת הקורונה לאורך ארבע מדידות אורך
קמחי, ש., מרציאנו, ה., אשל, י., עדיני, ב., (2021). חוסן, דחק ומיטביות בסיום סבב לחימה "שומר החומות"
Vigoda-Gadot & Levitats (2024). Like a bridge over troubled water: Wellbeing and trust in governance during turbulent times
Bibliographic details
Vigoda-Gadot, E., & Levitats, Z. (2024). Like a bridge over troubled water: Wellbeing and trust in governance during turbulent times. International Review of Administrative Sciences.
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic extended interest in the relationships between citizens and governments in turbulent times of crises and emergencies. While the pandemic generated a critical existential threat to the lives of many, it also had a significant effect on the quality of life and on the wellbeing of even larger populations.
This paper deals with the relationship between the wellbeing of citizens and three types of trust in governance (i.e. trust in political institutions, trust in public administration, trust in enforcement institutions) during the pandemic. We aim at advancing knowledge on both wellbeing and trust during crises, and more specifically on direct and indirect patterns of these important relationships. To do so, we suggest alternative models and a series of hypotheses aimed at examining them empirically. Two datasets on Israeli citizens are used. They were collected over two points in time during the heat of the pandemic and toward its decline and end (Study 1/t1; N = 1026 and Study 2/t2; N = 3024) and largely represent major sectors and ethnicities in the population.
The findings generally support a positive relationship between wellbeing and trust,but more importantly indicate that during crisis, trust in public administration and enforcement institutions mediates the relationship between wellbeing and trust in political institutions. We thus argue that the public service may act as a bridge between citizens’ wellbeing and political trust. In our view, the findings testify to the complexity of the wellbeing–trust relationship, especially in challenging times. Implications and directions for future studies are suggested.
Link: https://doi.org/10.1177/00208523231221971
Picard (2017). Disaster management, risk reduction and international disaster response laws in the Commonwealth
Mary Picard (2018): Disaster management, risk reduction and Bibliographic details:Bibliographic details:Bibliographic details:Bibliographic detailsBibliographic detailsBibliographic details:
Picard, M. (2017). Disaster management, risk reduction and international disaster response laws in the Commonwealth. Commonwealth Law Bulletin, 43(3-4), 403-437.
Abstract:
This paper considers the existence and use of disaster risk management laws across the Commonwealth. It commences by considering approaches to risk management and disaster response. It reviews international and regional disaster law, policy and tools. The paper examines national disaster risk management laws through the lens of a typology of laws, based on the complexity and scope of the disaster risk reduction and response system. It makes recommendations for Commonwealth countries relating to review of disaster laws, implementation of international frameworks, and the inclusion of disaster risk reduction, recovery, climate change, quality standards and the prevention of sexual and gender-based violence in disaster laws.
Webpage:
https://doi.org/10.1080/03050718.2017.1439362To link to this article: https://doi.org/10.1080/03050718.2017.1439362
Waismel-Manor et al. (2020). COVID-19 and Legislative Activity: A Cross-National Study
Bibliographic details:
Waismel-Manor, Israel and Bar-Siman-Tov, Ittai and Rozenberg, Olivier and Levanon, Asaf and Benoît, Cyril and Ifergane, Gal, COVID-19 and Legislative Activity: A Cross-National Study (July 2, 2020). Bar Ilan University Faculty of Law Research Paper No. 20-12.
Abstract:
Insufficient attention has been given to studying a vital organ jeopardized by COVID-19: legislatures. Legislatures across the globe have been shut down or limited due to COVID-19. In a comprehensive multidisciplinary study, exploring legislatures across 159 countries, we show that there is no causal relation between the severity of COVID-19 and limitations on legislatures’ operation. This suggests that legislatures are at risk of being shut down either due to unfounded fear from COVID-19 or as an excuse for silencing legislatures. We find that legislatures in healthy democracies are relatively immune to this risk, while those in frail democracies and authoritarian regimes are more at risk of becoming casualties of COVID-19. In partially free countries, the use of technology can mitigate this risk.
Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3641824 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3641824
זייצ'יק, בן-גל ושמואלי (2024). הזדמנות להתחדשות: סקירת ידע על שיקום חברתי-אקולוגי
פרטים בבליוגרפיים
זייצ'יק, דניאל, בן-גל, מיכל ושמואלי, דבורה (2024). הזדמנות להתחדשות: סקירת ידע על שיקום חברתי-אקולוגי. אקולוגיה וסביבה 15(1).
תקציר:
המאמר הנוכחי סוקר ספרות מדעית וידע על המושג שיקום חברתי-אקולוגי. בתוך כך, הוא מדגיש את החשיבות של בחינה מערכתית, הכוללת את הקהילה האנושית יחד עם המערכת הטבעית בתהליכי שיקום, ומסביר את המאפיינים והחשיבות של חוסן חברתי-אקולוגי. הקשר בין שיקום לחוסן הוא במעגל של היזון חוזר: החוסן משפיע על הצלחתו של השיקום, ותהליך השיקום קובע את חוסנה של המערכת ומשפיע על עתידה. בספרות זוהו שלושה מרכיבים שקיימים לפני האסון ומשפיעים על הצלחת תהליך השיקום שאחריו: פיתוח ידע, נתונים ותוכניות; ממשל מסתגל ואפקטיבי; כְּלִילָה (inclusion – ההפך מהדרה) חברתית. תהליך השיקום לאחר אסון יכול לשמש חלון הזדמנויות להתחדשות ולהטמעת שינויים לטובת המערכת החברתית-אקולוגית לטווח הארוך. במאמר מתוארים התנאים להבשלת חלון ההזדמנויות וכן היתרונות הטמונים בשיקום חברתי-אקולוגי. לצידם מובאות דוגמאות אקטואליות בהקשר של שיקום הנגב המערבי.
קישורים: https://magazine.isees.org.il/?p=58045
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4868952
The Dynamics of Social Capital and the Recovery of Israel’s Gaza Envelope: A Formative Evaluation
Funded by ISF (Israel Science Foundation) - 2024-2027
PI: Deborah Shmueli
Researchers: Danielle Zaychik, Yonat Rein-Sapir, Alex Altshuler and Michal Ben-Gal
This study aims to examine the dynamic relationship between social capital and the recovery process in the Israeli localities adjacent to the Gaza Strip, called the Gaza Envelope. As part of this process, the study assesses recovery progress against community-established goals and describes both how recovery has impacted social capital, as well as the role of social capital in facilitating recovery. At this point, there is a well-established pool of academic and gray literature concerning disaster recovery. Given that recovery is a multi-faceted process, the research base is broad and explores many aspects of disaster recovery. This research draws from literature concerning definitions of successful disaster recovery, disaster recovery as a participatory process, and social capital in disaster recovery. The literature on successful disaster recovery guides the study’s framing of recovery goals and assessment. Literature on participatory recovery processes set a base for public and stakeholder participation in the establishment of recovery goals. Finally, literature on social capital and disaster recovery informs our assumptions about how social capital influences disaster recovery. Gaps in our knowledge about the dynamic two-way relationship between social capital and disaster recovery set the stage for the contribution of the current research.
This research aims to assess the recovery of the Gaza Envelope through a social capital lens. To this end, the research will incorporate aspects of formative evaluation methodology. Formative evaluation seeks to assess an intervention or process before or during its implementation, subsequently influencing and improving its continued implementation. The proposed research assesses recovery of Gaza Envelope residents and communities as it occurs, against priorities selected by the residents of the area. In addition to providing feedback to policymakers and community leaders about the ongoing recovery process, the research will make the following theoretical contributions to existing academic literature about disaster recovery and social capital:
- The research will contribute to the underdeveloped literature detailing the impact of disasters and recovery on social capital. Although the literature suggests a dynamic nature to this relationship (Kawamoto and Kim 2019), few studies have explored this in depth with regards to multiple facets of recovery. The contribution of this research will address social capital impacts at both the individual and community levels.
- The research will contribute to literature on disaster recovery and social capital by examining the variation of effects by locality type.
- While much research has addressed the role of social capital in natural disasters, far less has assessed the role of social capital in manmade catastrophes. Social capital may have a different role in a large-scale man-made security event and enduring hostage situation than an earthquake or hurricane.
In addition to these theoretical contributions, the research has significant value for policymakers as they continue to shape the Gaza Envelope recovery process. Research findings will give feedback on recovery policies and can be used to adjust and adapt future policies and programs.
הדינמיקה בין הון חברתי והשיקום של עוטף עזה בישראל: הערכה מעצבת
מחקר זה נועד לבחון את הקשר הדינמי בין הון חברתי לבין תהליך השיקום ביישובי עוטף עזה. כחלק מתהליך זה, המחקר יעריך את התקדמות השיקום מול מטרות שהוגדרו ויוגדרו על ידי הקהילה ויבחן - הן כיצד השיקום השפיע על ההון החברתי והן את תפקידו של ההון החברתי בקידום תהליך השיקום. בשלב זה, ישנו מאגר מבוסס היטב של ספרות אקדמית וספרות אפורה בנושא שיקום מאסונות. מכיוון ששיקום הוא תהליך רב-ממדי, הבסיס המחקרי העוסק בו הינו רחב ומקיף היבטים רבים. מחקר זה מתבסס על ספרות העוסקת בהגדרות לשיקום מוצלח מאסונות, שיקום כתהליך שיתופי, ותפקידו של הון חברתי בשיקום מאסונות. הספרות על שיקום מוצלח מאסונות מנחה את מסגרת המחקר בנוגע למטרות השיקום וההערכה שלו. הספרות על תהליכי שיקום שיתופיים מספקת בסיס לשיתוף הציבור ובעלי עניין בקביעת מטרות השיקום. לבסוף, הספרות על הון חברתי ושיקום מאסונות מעצבת את הנחותינו לגבי האופן שבו הון חברתי משפיע על תהליך השיקום. הפערים בידע הקיים לגבי הקשר הדינמי הדו-כיווני בין הון חברתי לשיקום מאסונות יוצרים את הבסיס לתרומתו של מחקר זה.
Regulatory and Policy Frameworks for a Mid and Long-term Recovery after a Major Earthquake
Funded by the National Steering Committee for Earthquake Preparedness and the Israel Ministry of Science & Technology
PIs: Deborah Shmueli, Eli Salzberger, Amnon Reichman
Researchers: Danielle Zaychik, Michal Ben-Gal and Inbal Blau
(in cooperation with the Minerva Center for the Rule of Law under Extreme Conditions)
This project, co-funded by the Ministry of Innovation, Science and Technology and the Inter-ministerial Steering Committee for Earthquake Preparedness, began in 2022, and ended in 2024. The research examines long-term recovery after major earthquakes. It makes use of an extensive literature review and case study to identify important aspects for long-term recovery and creates a framework for pre-event long-term recovery planning. The first stage of the project included an international comparison of five countries' institutional and regulatory frameworks. The second stage of the project included the creation of typology for assessing long-term recovery, based on literature. This typology was then applied to the long-term recovery plans recently developed by the Israeli government. The third stage of the research consisted of an in-depth case study of the long-term recovery of Japan after the 2011 earthquake and tsunami. Policy recommendations and lessons for the Israeli context were extracted from the Japanese case.
Literature review I: International comparison of regulatory frameworks for recovery
Analyzing in-depth semi-structured interviews with experts as well as primary and secondary documents concerning the regulatory frameworks for recovery in Japan, New Zealand, Chile, Turkey, and Italy, four parameters were compared: recovery planning, governance, recovery processes, and resources.
Ten salient factors which influenced recovery trajectories were identified. These encompassed whether or not there existed: a designated body for emergency management; centralized power and responsibilities versus delegation of powers to local government; clear roles and designated areas of responsibility for bodies and institutions; legal tools and powers in the hands of authorized and responsible parties; a structured process for decision-making (including public/stakeholder involvement); a recovery/rehabilitation plan – developed either before or after the earthquake occurred – and the breadth of issues which it covered; data and knowledge driven decision-making, and a dedicated budget for rehabilitation.
Each of the five countries present a different model of operation: Japan is highly centralized, with a core legal structure which is dynamic and continuously updated; New Zealand is highly organized, providing blue-print plans for implementation by local authorities; Chile maintains that the governance structures in place during routine times should work for emergencies as well; Turkey’s model leans on international guidelines, and Italy is ad hoc – each event is treated differently.
Literature review II: Typology of earthquake recovery
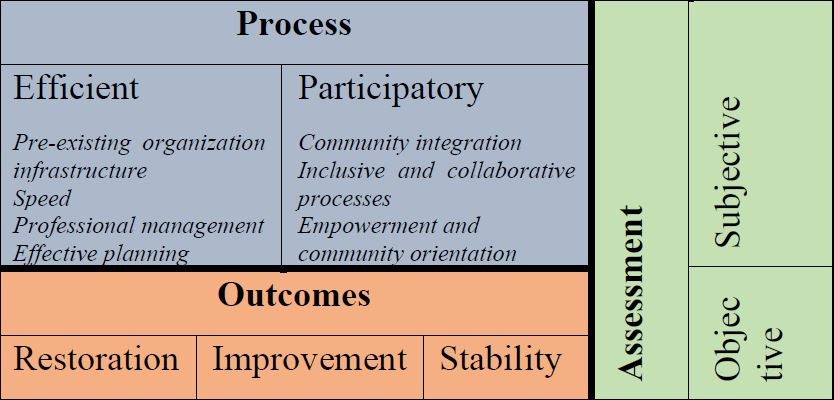
Based on literature review of successful earthquake recovery, a typology of disaster recovery was developed. The typology includes three major axes: aspects of recovery related to process, aspects of recovery relating to outcomes, and aspects of recovery that relate to evaluation. The process of recovery includes policies that create efficiency and/or a participatory process. Efficiency includes policies that promote speed, establish a pre-existing organizational infrastructure, cultivate professional management, and utilize effective planning. Participatory processes are created through community integration, inclusive and collaborative processes, and empowerment and community orientation. Outcome-related aspects of disaster recovery can stress restoration, improvement, or stability. Recovery evaluation can either be objective or subjective (or include both aspects). Evaluation is relevant to both the process and outcome aspects of recovery.
The typology described above is summarized in the following figure:
Application of second literature review on government plans for long-term recovery
Based on analyzing the government plans through the lens of the typology, the researchers recommended three primary ways to strengthen the government report: 1. Integrate more participatory mechanisms and community empowerment throughout recovery plans. 2. Integrate plans for making improvements (“Build Back Better”) throughout the recovery plans. 3. Integrate mechanisms and plans frameworks for evaluation throughout the government plans.
Japanese case study and recommendations for Israel
Based on written materials and studies available on the topic and a few in-depth interviews with experts, textual analysis of primary documents, and a literature review of academic studies, the case study includes nine chapters which describe the regulatory and organizational frameworks, the recovery process itself, primary policy tools implemented, community involvement in recovery, themes of the Japanese recovery and lessons that can be applied to Israel. Some of the interesting findings are listed below:
- Japan has a complete regulatory system for recovery (as opposed to narrow set of laws), at the center of which stands the 1961 Disaster Countermeasure Basic Act.
- After a disaster, a recovery advisory is convened, at the head of which presides the Prime Minister. After some disasters (such as the GEJE), a Recovery Agency was established, which managed all aspects of the GEJE recovery.
- There were four primary policy tools used during the Japanese recovery: Protection by physical means (such as seawalls), collective relocation, public housing projects, and land adjustments.
- Although the vision for recovery set out by the Japanese government included an emphasis on community empowerment and participation in the recovery process, this vision was not actualized in a meaningful way.
- Machizukuri (bottom-up participatory planning mechanisms) were an example of an exception, as they were successful in creating effective community empowerment and participation.
- Overall the Japanese recovery can be characterized as taking a centralized, top-down approach, emphasizing speed and efficiency, taking an engineering-based approach to Build Back Better, and a lacking integration of long-term planning into recovery plans.
Recommendations based on the Japanese case include: (a) plan for managing “time compression”, (b) lessons for financing mechanisms and structures, (c) plan for bottom-up recovery mechanisms, (d) pre-established structures, frameworks and arrangements are more efficient than ad-hoc arrangements, (e) create varied options for housing, (f) take a holistic approach to relocation and Build Back Better, (g) plan for participation (h) be aware of the complications of working with the public (i) prepare plans for the expected human resource shortage, (j) outline guidelines for improvement when striving to integrate a Build Back Better approach, (k) and integrate long-term planning in recovery planning.
יצירתו ותיקופו של מדד מתכלל למדידת חוסן ופיתוח מרחבי בישראל
צוות המחקר: דבורה שמואלי, דניאל זיייצ'יק, אפרת מישור, מיכל בן גל וסמדר אמיר
הוכן עבור אגף פנים, תכנון ופיתוח, משרד ראש הממשלה
במסגרת המחקר פותח מדד מתכלל לחוסן ופיתוח מרחבי בישראל, המיועד להערכת כלל הרשויות המקומיות בישראל. המדד נועד לשמש כלי אסטרטגי לטווח ארוך, אשר יסייע בגיבוש תמונת מצב מבוססת-נתונים, ובתוך כך לסייע בהכוונה, בגיבוש תכניות ובקביעת מדיניות מיטבית ומושכלת בתחומי חוסן ופיתוח מרחבי. המדד אשר פותח במחקר כורך שני מושגים שונים לצורך גיבוש מדד אחד – האחד הוא חוסן והשני פיתוח מרחבי. במסגרת בניית המדד המתכלל המושג חוסן הוגדר כיכולת החברה למזער את ההשפעה השלילית של הפרעה תוך שמירה על רציפות תפקודית במהלך ההפרעה ולאחריה. המושג פיתוח מרחבי הוגדר כפעולה יזומה השואפת למיצוי והרחבת הפוטנציאל הכלכלי, החברתי והסביבתי של אזור מסוים בהווה ובעתיד.
המדד המוצע מורכב מארבעה תחומים מרכזיים: כלכלה; חברה; שלטון מקומי; ותכנון, סביבה והמרחב הבנוי, אשר מורכבים ממספר אינדיקטורים. ניתוח הנתונים מפריד במלואו בין התחומים ומספק דירוג של חוסן ופיתוח מרחבי לכל 255 הרשויות המקומיות בישראל בכל תחום. במילים אחרות, ארבעה ציונים נפרדים ששקלולם יוצר מדד אחד. המדד מותאם לכלל מדינת ישראל ונמדד כאמור, ברזולוציית הרשות המקומית. כך , הוא מאפשר השוואה רוחבית של רשויות בנוסף להשוואות על פי ציר הזמן.
היתרון המרכזי ביצירת מדד מתכלל הוא האפשרות לקבל תמונה כוללת על נושא מורכב, אשר מכיל משתנים ופרמטרים רבים. בנוסף, כאשר מתבצעת אינטגרציה בין מדדים ותחומים שונים תוך התחשבות במשקלם היחסי, מתקבל מדד מדויק יותר שמשפר בסופו של דבר את יכולת הניתוח וקבלת ההחלטות. התוצר הסופי של המדד הינו דירוג הרשויות המקומיות בסקאלה שנעה בין 0-100 . ציון 100 ישקף חוסן ופיתוח מרחבי שאינם דורשים שיפור (אידאל) בעוד שציון 0 ישקף מצב שלרשות אין כלל חוסן והפיתוח המרחבי שלה הוא אפסי. בנוסף כאמור, המדד מאפשר שימוש בכל תחום מארבעת תחומי המדידה בנפרד על פני אותה סקאלה.
יצירתו של המדד בוצעה על ידי מרכז הידע והמחקר הלאומי בתחום ההיערכות למצבי חירום באוניברסיטת חיפה בשיתוף פירמת ייעוץ Tefen, הקואליציה הישראלית לטראומה, וד"ר אפרת בליטשטיין-מישור, ובהנחייתם של גלבוע זינגר ו ד"ר ניר קפלן מהצוות לתכנון ופיתוח מרחבי באגף פנים, תכנון ופיתוח במשרד ראש הממשלה. הפרויקט בוצע כחלק ממחקר מלווה להחלטת ממשלה 566 מיום 20.11.2020 20.11.2020 לחיזוק החוסן האזרחי באזור עוטף עזה.
לדו"ח המחקר: פיתוח המדד ופיילוט לבחינתו - אוקטובר-2023
לתיקופו ומדידתו של המדד המתכלל על פי נתוני כלל הרשויות המקומיות בשנת 2019
לתיקופו ומדידתו של המדד המתכלל על פי נתוני כלל הרשויות המקומיות בשנת 2021
Resilience and Spatial Development Indicators for Israeli local authorities
Funded by Israel Prime Minister Office, Department of Home Affairs, Planning and Development, in cooperation with Tefen consulting firm
PI: Deborah Shmueli
Researchers: Danielle Zaychik, Efrat Mishor and Michal Ben-Gal
This project creates a comprehensive index that measures both resilience and spatial development for the State of Israel at the local level. The creation of the index included a wide review of indices for development and resilience both globally and in Israel. After consultation with experts in Israel, and availability of existing data, 62 indicators were selected, in four areas: economy, society, local government, and environmental planning and the built-up space. After a pilot with 16 varied local authorities and validation of the index, the Prime Minister’s Office (with scientific support of the Center) applied the index to all the local authorities in Israel. This measurement will serve as a baseline for national follow-up on the impacts of national and local programs on the localities in Israel, as well as be used by local authorities to assess their level of resilience and development.
For more details see in Hebrew: יצירתו ותיקופו של מדד מתכלל למדידת חוסן ופיתוח מרחבי בישראל